Protecting the precious
environment
Decarbonization
We are working to reduce CO2 emissions to realize a decarbonized society.
Haseko Group’s greenhouse gas emission reduction targets

Reduction targets were set using greenhouse gas (CO2 (*1)) total emissions as a metric, and the 2030 reduction targets were approved as science-based targets by the SBT (Science Based Targets (*2)) initiative.
We have also established and are moving forward with a concrete plan for achieving the reduction targets.
(*1) CO2 is the principal greenhouse gas in the world and accounts for
the majority of the Haseko Group’s emissions. (*2) It was jointly established in
2015 by CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, the World Resources Institute (WRI),
and the World Wildlife Fund for Nature (WWF) to encourage companies to set
science-based greenhouse gas emission reduction targets toward the goals of the
Paris Agreement “limiting global temperature rise to well-below 2°C above
pre-industrial levels and pursuing efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C.”
Targets and initiatives for achieving them
We have set the following greenhouse gas emission reduction targets with fiscal 2020 as the base year, and are promoting reduction initiatives.
| Scopes covered |
Targets | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Actual greenhouse gas emissions in Fiscal 2020 (base year) | FY2030 target | FY2050 target | |
| Scope1+Scope2 | 60,382 | Reduce 42% from base year | Reduce 100% from base year |
| Scope3 | 5,495,690 | Reduce 13% from base year | Reduce 37% from base year |
(*3) Scope 1: Direct emissions by the business itself
(*4) Scope 2: Indirect emissions associated with consumption of electricity, heat or steam purchased from outside
(*5) Scope 3: Indirect emission other than Scope 1 or 2 (supply chain emissions related to the business’s activities)
- Related information
The Haseko Group’s Climate Change Response: HASEKO ZERO-Emission
To read more about the Haseko Group’s initiatives to address climate change, please click the Related information link below.
CO2 emissions
Unit:t-co2
| Haseko Group | FY2020 (base year) |
FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1 | 38,596 | 40,487 | 34,486 | 52,224 | 45,571 |
| Scope2 | 21,786 | 24,258 | 18,302 | 8,349 | 4,766 |
| Scope3 | 5,495,690 | 6,175,367 | 5,629,382 | 5,294,469 | 5,685,999 |
| Haseko Corporation | FY2020 (base year) |
FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope1 | 33,636 | 34,379 | 30,869 | 45,449 | 39,886 |
| Scope2 | 10,366 | 11,531 | 6,129 | 680 | 493 |
| Scope3 | 3,522,486 | 4,679,218 | 4,179,710 | 4,088,921 | 4,521,843 |
*The target scope within the Haseko Group is Haseko Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries (excluding overseas subsidiaries).
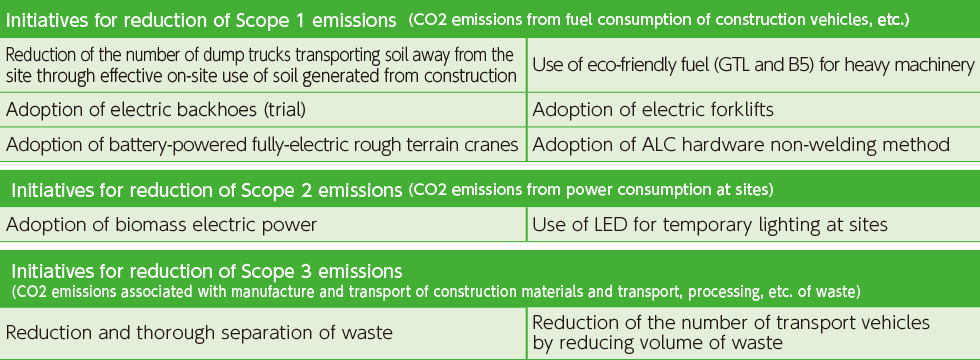
Initiatives at the construction stage
Initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions at construction sites
The Haseko Group is promoting the following initiatives at certain sites to reduce CO2 emissions at construction sites. Going forward, we will continue to increase the number of cases of adoption and promotion of these initiatives, while taking the scale and location of project into consideration.



Adoption of “H-BA Concrete,” an environment-conscious concrete
Produced by blending ordinary Portland cement and blast furnace cement type-B, H-BA concrete is so versatile that it can replace conventional concrete. It is eco-conscious concrete that reduces CO2 emissions derived from concrete materials by approximately 20%.
To date, it has been used in projects including a part of the common-use areas of “Renai Yokohama Totsuka” (Totsuka-ku, Yokohama City, Kanagawa; total 439 units) and the entirety of the “Gakuen Higashimachi Project” (foundations and above-ground framework), a rental condominium building targeting students (Nishi-ku, Kobe City, Hyogo; total 120 units). In August 2022, H-BA concrete obtained the “Special Evaluation Method Certification*2,” which is recognized as an alternative evaluation method to methods that comply with the “Evaluation Method Criteria*1,” from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. This certification allows it to be used in for-sale condominiums that use dwelling performance indications.
Based on the Special Evaluation Method Certification, “H-BA concrete” has been adopted for the first time as sale condominiums for the entirety of the above-ground framework in the THE-KENSINGTON-RESIDENCE-KAMIIKEDAI (Ota-ku, Tokyo; total 42 units) in the Tokyo area, and the “Renai Esaka Enokicho” (Suita City, Osaka; total 149 units) in the Kansai area. We will continue to utilize H-BA concrete in the Group’s projects. In addition to Group business projects, we will work to popularize H-BA concrete in the projects of other companies to promote the reduction of greenhouse gas (CO2) emissions across the entire supply chain.
In order to achieve the Haseko Group’s greenhouse gas emission reduction targets, we will work to further promote the adoption of H-BA concrete, aiming for a usage rate of at least 50% by fiscal 2030.
*1 Evaluation Method Criteria: Criteria for methods of evaluating housing performance to be indicated in accordance with the Japan Housing Performance Indication Standards stipulated in the Housing Quality Assurance Act.
*2 Special evaluation method certification: Certification method approved on an individual basis by the Minister of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism for new materials and construction methods (e.g., structural safety, reduced deterioration, thermal environment, sound environment) that cannot be evaluated in accordance with evaluation method criteria stipulated in the Housing Quality Assurance Act.
Amount of H-BA concrete used and its impact on reduction of greenhouse gas (CO2) emissions
This table can be scrolled
| Fiscal year | Volume used (㎥) | CO2Reduction of CO2 (t-CO2) |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 125 | 6.2 |
| 2020 | 25 | 1.1 |
| 2022 | 2,945 | 162.6 |
| 2023 | 2,361 | 140.8 |
| 2024 | 37,594 | 2,186.2 |
| Total | 43,050 | 2,496.9 |
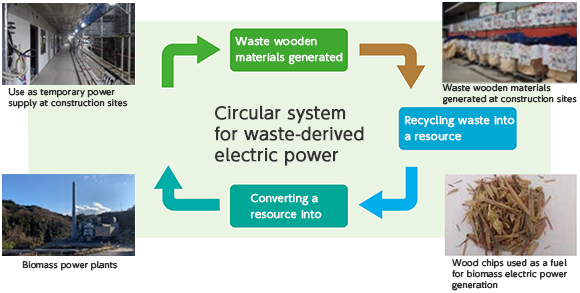
Introduction of biomass electric power
Initiatives for biomass power generation through the recycling of wood waste
In cooperation with an outside power generation company, we have introduced a resource recycling initiative to utilize renewable energy from biomass power generation, which uses waste wooden materials generated at construction sites as part of its fuel, as a temporary power supply at construction sites. Power generation through this initiative results in lower CO2 emissions than conventional thermal power generation, which will reduce CO2 emissions generated by the supply of electricity.

Participation in the biomass power generation business
Haseko Corporation participates in biomass power generation business with the goal of achieving carbon neutrality.
We participate in a woody biomass power generation business in Ikoma city in Nara undertaken by TJ Group Holdings Inc. Scrap wood and unused timber from the Kinki region will be used as fuel for generating power in the business, which makes it possible to supply locally produced and locally consumed electricity, including fuel for power generation, for users in the Kinki region. (Commercial operations started in April 2025.)
In Matsusaka City in Mie, we participate in a decarbonized power source development business undertaken by Power Aid Mie that uses hybrid fuel of only NON-FIT wood and manufacturing byproducts. In this business, waste recycled wood chips and plastic chips generated from various construction sites will be repurposed as fuel, leading to the reduction of the administrative burden of waste disposal operation and the contribution to the creation of a local circular resource and energy economy. (Commercial operations started in April 2025.)
We will continue our efforts to contribute to creating carbon zero cities through initiatives such as biomass power generation business.
Development and use of technology for the solidification of construction sludge using bamboo chips
In cooperation with Professor Kenichi Sato of Fukuoka University’s Faculty of Engineering, the Company has developed a new technology that uses bamboo chips*1 to solidify construction sludge.
By replacing half of the cement-based solidifying agent added to construction sludge with bamboo chips, this technology is expected to halve the annual CO2 emissions generated from cement-based solidifying agents, reducing them from approximately 8,000 t-CO2 to 4,000 t-CO2. This is equivalent to the amount absorbed by approximately 285,000 Japanese cedar trees in one year. Furthermore, applying a second solidification treatment to construction sludge delivered to intermediate disposal sites will make it into reclaimed soil*2 suitable for use as embankment material. Since bamboo absorbs carbon dioxide and stores carbon during its growth process, bamboo chips used in reclaimed soil can be expected to contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society in the role of an “absorbent” *3 in carbon neutrality.
This technology will first be used at a new condominium construction site in Ichikawa, Chiba, followed by sequential use at our other construction sites. In addition, the use of bamboo chips can significantly contribute to resolving the problems caused by neglected bamboo forests. To this end, we will promote initiatives aimed at solving regional issues by collaborating with Asuka Village in Nara, Fukuoka Prefecture, and other entities that have signed agreements aimed at regional revitalization and regional development.
- Bamboo finely chopped into pieces about 5 millimeters in size using a grinding mill or other means
- Sludge, concrete, and other industrial waste generated at construction sites that has been dried, pulverized, and in some cases mixed with other materials to form a substance with a similar shape to soil
- The following prior research was referenced in the calculation of decarbonization results. When the carbon content of bamboo is estimated at 47% of its dry mass, its carbon storage capacity is approximately 39,000 t-CO2. / Goto et. al. (2008). Study on estimation of biomass and carbon storage in abandoned bamboo stands ecosystem. Japanese Agricultural Systems, Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 243-252.

Benefits of using this technology
- (1) Reduces CO2 emissions by reducing the amount of cement-based solidification agents used
- (2) CO2 absorbed in the bamboo growth process is fixed underground
- (3) Significantly contributes to the resolution of the problems caused by neglected bamboo forests as technology that uses felled bamboo effectively
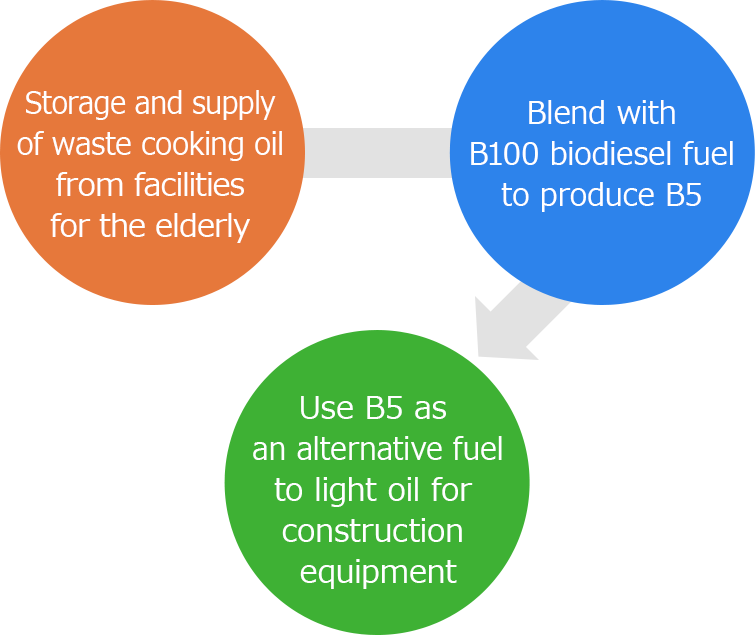
Building a waste cooking oil utilization system to provide an alternative fuel to light oil
We have built a waste cooking oil utilization system in which the waste cooking oil generated by kitchens of Haseko Senior Well Design’s facilities for the elderly is supplied to construction sites as an alternative fuel to light oil for construction equipment, after being refined into biodiesel fuel (B5)* by Sanwa Energy.
Using this biodiesel fuel can lead to a 5% reduction in CO2 emissions compared to light oil.
We will continue with further studies on similar initiatives to utilize waste cooking oil emitted by the condominiums developed by Haseko Real Estate Development, Sohgoh Real Estate, and other Group companies, as well as the condominiums managed by Haseko Community.
*A blend of fuel that consists of light oil mixed with 5% or less biodiesel fuel
Reduction of CO2 emissions relating to transport
As close to 90% of CO2 emissions at construction sites are generated by consumption of light oil, reducing the amount of light oil used will significantly affect CO2 emission reductions.
Industrial waste generated at construction sites is separated by type (wood waste, waste plastics, mixed waste, etc.) and processed by designated companies. Of these, mixed waste is generated over an extended period of time spanning the commencement of construction to completion of the building, notwithstanding significant reductions in volume generated. We reduce the distance over which waste is transported by selecting the waste processing company nearest to the construction site, from a pool 6 companies and 12 plants in the Tokyo region and 6 companies and 11 plants in the Kansai region.
In addition, soil generated from excavation work is used as backfill material on the site to the greatest extent possible. By improving the efficiency of waste accumulation and transportation, less dump trucks are required, thus reducing CO2 emissions. In addition, most of all waste soil that is removed from construction sites is processed for use in land reclamation, which is destructive on the environment. Thus, by reducing the amount of waste soil that leaves our construction sites, we contribute to environmental protection.
Reducing rainforest-sourced materials and environmental burden
Plywood for concrete formwork is made of materials sourced from
rainforests. Loss of vast rainforests means losing a huge CO2 absorber,
so there is an urgent need to preserve them also from the viewpoint of biodiversity.In the construction division, we are advancing our efforts to use
precast concrete (PCa) units for handrails and edges of corridors and balconies,
decorative columns, exterior stairs, floors and PCa for edges of corridors, in addition to employing the ALC method for non-load bearing walls. We also use steel formworks and
plastic formworks where possible in order to reduce the use of plywood formworks
made of rainforest wood.
Replacing wooden formworks by industrial products or alternative formworks or other products has led to reduced waste in preparing formworks and fewer concrete mixer trucks, which contributes to reduction of industrial waste and CO2 emissions.


Green procurement initiatives
Initiatives to select materials with smaller environmental footprint is called green procurement. For the fiscal year 2024, we investigated the following items and determined their quantities as part of our green procurement efforts.
Going forward, we will review and add green procurement materials as necessary in consideration of green procurement results, social trends and other factors.
| Item | Unit | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | FY2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel for electric furnace (reinforcing steel) |
1,000t | 169 | 195 | 196 | 197 |
| Steel for electric furnace (steel frame) |
1,000t | 2 | 5 | 12 | 21 |
| Blast furnace cement and freshly-mixed concrete |
1,000m3 | 225 | 208 | 223 | 274 |
| Recycled tiles | 1,000m2 | 220 | 246 | 218 | 213 |
| Recycled plasterboards | 1,000m2 | 4,900 | 4,828 | 4,971 | 5,023 |
| Water-saving toilet bowl | 1,000units | 16 | 17 | 17 | 17 |
| Water-saving showerheads | 1,000units | - | - | - | 19 |
| LED lighting equipment | 1,000units | 304 | 176 | 190 | 234 |
Blast furnace slag cement type B
Blast furnace slag cement type B, which is superior against cracks and in terms of chemical resistance, is mainly adopted in concrete piles. CO2 generated during cement production is the largest in volume during the manufacturing process of clinker, an interim product of cement. The production of blast furnace slag cement involves mixing large volumes of blast furnace slag fine powder into normal cement, which leads to a much lower composition ratio of clinker than in normal cement, and in turn, reduction of CO2 emissions.
In fiscal 2024, adoption of blast furnace slag cement type B was 196,175 m3 in the reduction of CO2 emissions by 22,168 tons.

Design-stage initiatives
Utilizing CO2 Emissions Calculation Sheet
In April 2017, we revised Haseko Corporation’s proprietary “CO2 Emissions Calculation Program,” which we had continued to operate since its development in 2011. Based on the revision, we began calculating the CO2 reduction rate based on the “CO2 Emissions Calculation Sheet” using the figures calculated in accordance with the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings. We have been implementing the revised program since then.
In fiscal 2023, we set CO2 reduction rate of 10% or higher (Ratio of standard values under the Building Energy Conservation Act) as our numerical target and implemented it in 106 projects of condominiums designed between April 2023 and March 2024 (82 projects in the Tokyo region and 24 projects in the Kansai region).
| Tokyo region | Kansai region | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 reduction volume (FY2024) | 12,558t-CO2/year | 4,230t-CO2/year | |
| Standard value under Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings |
CO2 reduction rate | 27.6% | 29.3% |
* The CO2 Emissions Calculation Sheet is a sheet for computing the CO2 reduction rate by converting the standard value and the design value of primary energy consumption of condominium unit areas and communal areas calculated with respect to each project using a Web program in accordance with the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings into CO2 emissions (t-CO2/year).
Promotion of wood use in construction of condominiums
Since 2014, the Haseko Group has been working to promote the use of wood and wood materials in condominiums. Our track record so far includes the use of hybrid structures of wood and reinforced concrete not only in condominium common buildings, but also in common areas and on the upper floors of private-use areas. As of July 2025, we have 20 completed properties and 9 properties under construction.
In March 2025, we completed the BRANSIESTA MEGURO CHUOCHO rental condominium, which features a fire-resistant wooden structure on its top four floors. We expanded the HASEKO-version BIM system to make it compatible with wooden structures, and utilized it in the basic design and detailed design phases of this project. The condominium was selected for the FY2022 3rd Term Project for the Promotion of High-Quality Wooden Buildings, a subsidy program offered by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism. In the future, in addition to taking on the challenge of adopting wooden structures in high-rise buildings, we hope to expand its application to include for-sale condominium development as well as rental condominium development.

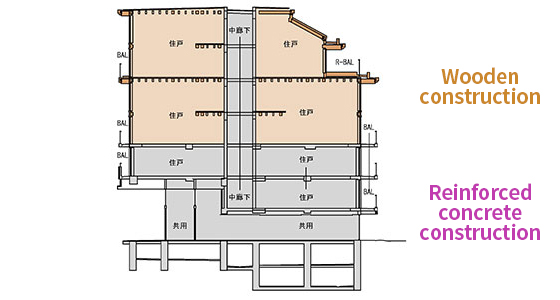

Structural diagrams of BRANSIESTA MEGURO CHUOCHO
Operationalization of Support Tools for Energy-Saving Performance Calculation
We have developed an energy-saving calculation system which is linked to BIM (Building Information Modeling) data. We make notifications in accordance with the Act on the Improvement of Energy Consumption Performance of Buildings and examine thermal insulation specifications using this system. We developed a tool with the aim of further labor saving through automation of calculation as well as visualization of calculation results and launched it at design divisions in the East and West Japan in January 2020. The operation of this tool has enabled a 50% reduction in work hours and a reduction in input errors through automated calculations. We will use these technologies to promote optimal design that meets energy-saving performance requirements.
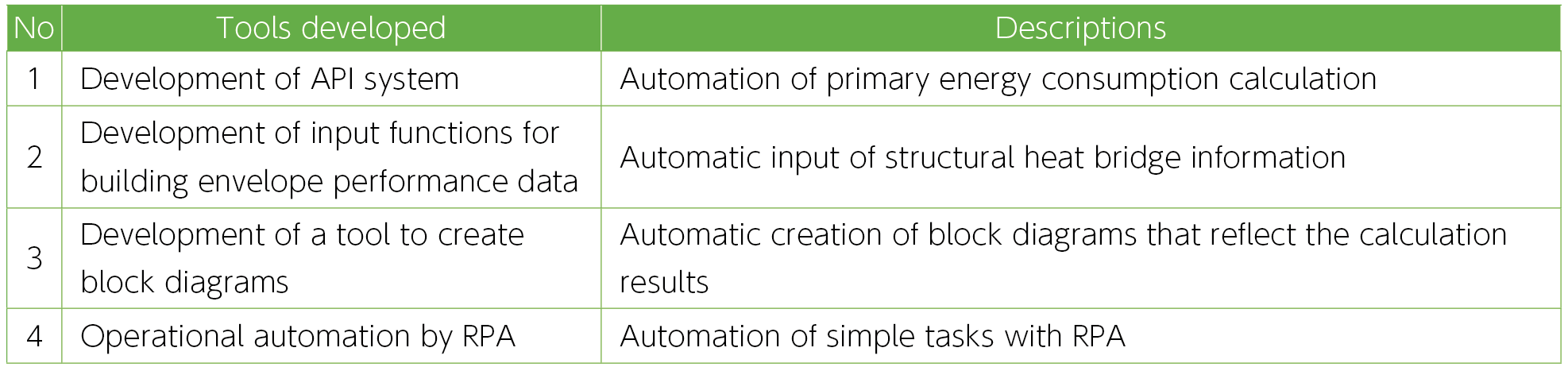
Initiatives conducted by all Group companies
The Haseko Group is working with all group companies to reduce CO2 emissions from office activities.
Switching to using 100% renewable energy
To reduce CO2 emissions generated from electricity consumption, we aim to switch to using 100% renewable energy at offices and construction sites.
The use of 100% renewable energy was achieved in May 2023 for Haseko Corporation’s construction sites, and in March 2025 for the Haseko Group’s construction sites.*
We plan to switch to 100% renewable energy, including in all offices, by the end of 2026.
* This excludes sites pending requests to switch to renewable energy electricity subsequent to the commencement of construction and sites switching to (nonrenewable) power company supply before delivery.
- Related information
Initiatives to reduce CO2 emissions through activities at offices
The Haseko Group is promoting energy saving in offices, centering on the “activities by the Response to Climate Change Office Working Group (WG).”
We obtained SBT certification in fiscal 2022 and calculate and compile the volume of CO2 emissions by aggregating the monthly total energy consumption of each company. In this way, we are able to visualize our progress and are working hard to reduce our energy consumption volume.
Switching to using renewable energy
In fiscal 2024, to promote the switch to 100% renewable energy at offices and company-owned facilities, we switched to renewable energy with a focus on office buildings owned by the Company and rented by the building. In cases where it is difficult to switch to renewable energy, such as at rental properties, we substantially switch to renewable energy through the purchase of non-fossil certificates.
In fiscal 2024, we reduced Scope 2 emissions in Group offices by 21.3% compared to the previous fiscal year.
Replacing company vehicles with electric and hybrid vehicles
We introduced eight electric vehicles at the Shiba Head Office in April 2024, and we plan to replace two gasoline vehicles at the Hiranomachi Building in Osaka with electric vehicles in September 2025.
Regarding shuttles used by Furusato for its day service for people with dementia, the 21 out of 139 company vehicles that were hybrids in March 2023 will increase to 51 in fiscal 2024. Furthermore, we will replace all company vehicles used as shuttles with hybrid vehicles by March 2025.
In fiscal 2024, we reduced Scope 1 emissions in Group offices by 2.6% compared to the previous fiscal year.
Reduction of CO2 by Donating PET Bottle Caps
The Haseko Group donates PET bottle caps as a part of its daily ecological activities. In fiscal 2024, we collected PET bottle caps equivalent to 1,188 kg from our Offices and construction sites and donated them to the Japan Committee, Vaccines for the World’s Children (JCV).
This contributed to the reduction of CO2 emissions resulting from incinerating PET bottle caps by 3,743 kg.
Initiatives in connection with Haseko Anshindeli’s rice paddy fields
Haseko Anshindeli is a company engaged primarily in the cultivation of rice, and was established in January 2015.
In Japan, conventional agriculture that utilizes agricultural chemicals and chemical fertilizers is the norm. However, Haseko Anshindeli uses decarbonized and environmentally-friendly farming techniques.
An example is the rice farming technique of “mid-season draining” in which draining water from the paddies at a specific period in the middle of summer for around one to two weeks in order to improve yield and quality. Haseko Anshindeli extends this period by around one week, which minimizes the impact on rice yield while reducing the amount of methane produced.
We achieved a reduction of 48.4 t-CO2 in fiscal 2024 as a result of decarbonized and environmentally-friendly farming techniques, at the core of which is this “extended mid-season draining” technique.
Goals for future initiatives
As around a quarter of greenhouse gases emitted worldwide are attributable to the agricultural sector, we aim for further reduction while continuing with business operations by measures such as using compost and reducing the volume of chemical fertilizers, and make progress in transitioning to organic farming to achieve better decarbonization.
- Sustainability TOP
- Message from the Management
- Message from the Officer in Charge of Sustainability Promotion
- Haseko Group's Sustainability Management
- Climate Change Response
- The Digital Transformation Strategy of the Haseko Group
- D&I at the Haseko Group
- Creating attractive living spaces
- Building a company worth working at
- Protecting the precious environment
- Nurturing a culture of trust
- ESG Data and Disclosures
- External Evaluations and Awards
- Integrated Report
- Philosophy and Policies
- Special feature archives